What Groups Did You Click Through to Get to Classes Mammalia and Reptilia?
The science of classifying organisms is called taxonomy. Every species discovered so far are classified into 5 kingdoms – i among them is Kingdom Animalia or Brute kingdom. The members of kingdom Animalia are further classified into different Phyla,Form, Order, Family, and Genus based on certain identifiable characteristic features.
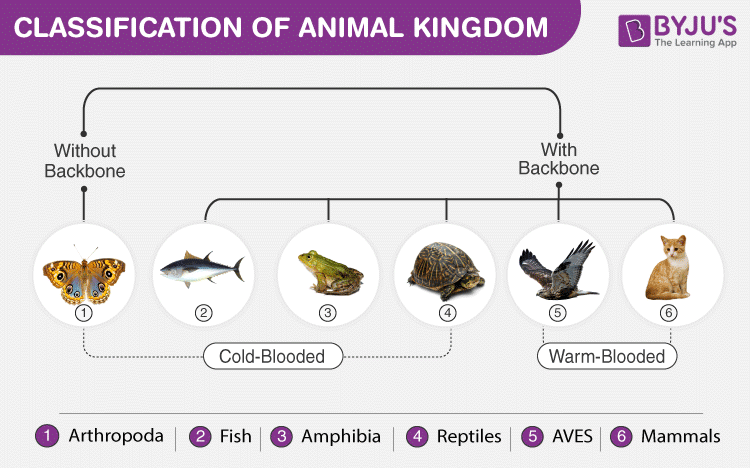
Ane of the almost fundamental forms of nomenclature of animals is the presence or absence of the notochord. Hence, two major groups exist, namely: Chordates and Non-chordates.
Non-chordates and the Chordates
The notochord is a flexible rod made out of a material like to cartilage. If an animal has a notochord during any stage of its life, it is classified as a chordate. Reverse to popular belief, chordates practise not exclusively include vertebrates.
There are invertebrates that possess a notochord during some point in their lives and hence, are classified equally chordates. Thus all vertebrates are chordates merely not all chordates are vertebrates.
Non-chordates
Non-chordates are animals without a notochord – the rod-like elastic structure that supports the body. This phylum consists of a small group of worm-like, marine species with an organ-organisation level of organisation.
Members of phylum Porifera, Coelenterata, Ctenophora, Platyhelminthes, Aschelminthes, Annelida, Arthropoda, Mollusca, Echinodermata and Hemichordata fall under Non-chordates.
The general characteristic features of Non-Chordates are:
- They are cylindrical, triploblastic, coelomate, or pseudocoelomate animals.
- Respiration in these animals takes place through gills, trachea or body surface.
- Most of the times, sexes cannot be distinguished among the members.
- Modes of reproduction involve sexual and asexual
- Fertilization is external, though internal fertilization also occurs in some species.
- The body of not-chordates mostly includes an open up type of circulatory organisation.
Chordates
Chordates are animals characterized by the presence of notochord at some stage during their development. Members possess a hollow nerve cord and pharyngeal gill slits. The other general characteristic features of Chordates are as follows:
- They are bilaterally symmetrical, triploblastic, and coelomate with the organ-system level of organization.
- They hold a post-anal tail
- The body includes a closed circulatory system.
- In some members of Phylum Chordata, the notochord is nowadays only in the larval tail, and in some, it is nowadays throughout their life from head to tail region.
- Chordates have many sub-divisions and Protochordates are one of the primeval to evolve.
Phylum Chordata is divided into three subphyla: Urochordata, Cephalochordata, and Vertebrata.
Subphylum – Urochordata
It is also referred to as Tunicata which are marine animals. The trunk of these animals is surrounded by a leathery covering (like to a tunic, hence the name). Larvae are gratis-pond, the notochord is present only in the tail of larvae and after settling on the seabed, they become transformed into sessile adults. They are mostly hermaphrodites.
Examples include – Ascidians, Doliolum, Oikopleura, etc.
Subphylum – Cephalochordata
Information technology mainly consists of small, fish-like marine animals in which the notochord is extended along the entire body. The animals also have throat, which is large with numerous gill- slits. Members of this subphylum have separate sexes.
Example include – Amphioxus or lancelet.
Subphylum – Vertebrata
In this subphylum, the notochord is present in the embryonic stages and is replaced past a vertebral cavalcade in the developed. They have 2, three or iv chambered eye, paired appendages for locomotion and kidneys for excretion or osmoregulation.
Vertebrates Classification
The subphylum Vertebrata is divided into five classes of vertebrates. These 5 classes of vertebrates comprise of all the species of animals and have developed vertebral column as well as an internal skeleton.
At that place are over 66,000 species of vertebrates identified under phylum Chordata till date. The defining feature of vertebrates is that their bodies are bilaterally symmetrical, coelomic, triploblastic, and with complex differentiation of body tissues and organs.
Other characteristic features of vertebrates are:
- Presence of a true vertebral column and internal skeleton with musculus attachment points for body move.
- A front end-side muscular eye with two, three or iv chambers.
- Kidneys for excretion and osmoregulation
- A paired appendages which may exist fins or limbs.
- Possess notochord during the embryonic stage.
- Vertebrates are the simply chordates to possess a encephalon as a function of the primal nervous system.
Classification of Vertebrates
- Pisces
- Amphibia
- Reptilia
- Aves
- Mammalia
Grade Pisces (Fishes)
They are aquatic animals, having a streamlined body and a pair of fins which are used for propulsion and movement. Furthermore, fish are cold-blooded, but the discovery of a new species in 2015 has inverse this perception. The opah or the moon-fish is a fully warm-blooded fish capable of regulating its body temperature.
Endoskeleton may exist cartilaginous or bony and respiration occurs through gills. They do not possess eyelids because the surface of the eye is to be kept moist all the time.
Examples of Form Pisces includes dogfish and Rohu.
Read More: Pisces
Class Amphibia
They normally comprise those organisms which are cold-blooded and require an aquatic habitat to lay eggs. These organisms are mainly characterized by the two pairs of limbs, shine and moist skin for respiration. They also possess protruding eyes which are protected by usually more than than one pair of eyelids. (Frogs have 3).
Examples of Class Amphibia are frog, toad, and salamander.
Further Reading: Amphibia
Class Reptilia
Course Reptilia comprises those organisms which are ectothermic in nature (cold-blooded). They are characterized by osteoderms which form scales, bony plates or scutes on the skin. Reptiles also lack an external ear and some reptiles such every bit snakes are actually "deafened" and instead, pick up vibrations through the ground. Another amazing sense that only snakes possess is Thermoception. This ways that snakes can come across infrared radiations emitted by objects or prey.
Examples of Class Reptilia are Tortoise, Wall cadger, Snake, etc.
Extended Reading: Class Reptilia
Course Aves (Birds)
About members have a streamlined body specially designed to offering low air resistance during flight. In such birds, the forelimbs are modified into wings, with the ability coming from breast muscles. Feathers play important roles, from flight, thermal insulation to water-proofing. All members of this class are warm-blooded and are able to regulate their body temperature.
Aves have beaks, which are used for diverse functions such equally preening and feeding. Furthermore, birds are considered to be the living relatives of dinosaurs (evolved from a group of meat-eating dinosaurs called the theropods).
Examples of Class Aves are Parrot, Pigeon, Duck, etc.
Read More: Aves
Class Mammalia
These organisms are distinguished by the presence of mammary glands. They take ii pairs of limb for walking, grasping, swimming, flying, etc. Digits are provided with claws, nails or hooves. Peel is covered past pilus and they have an external ear called pinnae. They are warm-blooded animals.
Examples of Class Mammalia include monkeys, lions, bats, squirrels and humans.
Further Reading: Mammalia
Acquire more nearly Classification of the Animal Kingdom and other related topics at BYJU'S Biology
Source: https://byjus.com/biology/classification-of-animal-kingdom/
0 Response to "What Groups Did You Click Through to Get to Classes Mammalia and Reptilia?"
Post a Comment